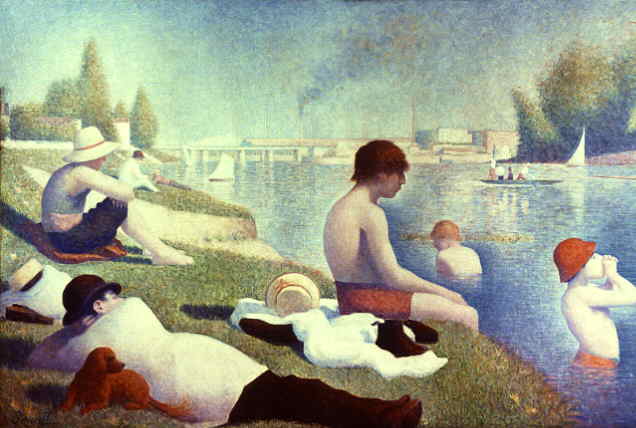 


 |
Neoclassicism (1750-Current):
Neoclassicism often depicted serious events or people.
The different wars that occured were often a focus in Neoclassicism paintings.
This style can also be described as simple, yet elegant.
Artists (click on the link for more info):
Romanticism (1800-1850): Romanticism paintings emphasized imagination, freedom, and emotion.
Paintings often had a simple, direct language that
brought intense feelings into their viewers.
Romanticism was a revolt against the enlightenment and a reaction to rationalization of nature,
so paintings often glorified the sense of peace and nature.
Artists (click on the link for more info):
Realism (1850-1880):
Realism often showed the world as it really was.
These paintings were not always bright and happy,
They often focused on the more dark, harsh side of the world.
Artists (click on the link for more info):
Impressionism (1860-1900):
Impressionism was usually in bold colors but didn't involve much detail.
Pictures consisted of outdoor scenes and landscapes.
A lot of pictures had a certain "shimmer" to them.
Pointillism (1880):
Pointillism was painted using a series of colored dots, varying in size.
From a distance the painting looks solidly painted,
but a closer view you can see the different dots.
Pointillism paintings were often painted in colors based
on impressionism coloring schemes.
Post-Impressionism (1880-1920):
Starting in the 19th century was mainly painted
as still lives and landscapes.
The colors were very varies but with a lot of shadow.
Artists (click on the link for more info):
Vincent Van Gogh Art Nouveau (1890-1914):
Art Nouveau was an art movement that occured in response to
advances from the Industrial Revolution. The style was inspired by the dynamic
color of Japanese art and the elegant patterns in Islamic art.
Art Nouveau focused on nature with fine craftmanship and individual creativity
and often helped explore the inner world of spirit, myth, and dreams.
Analytical Cubism (1910-1912):
Analytical Cubism style had right angles and strait lines.
The style showed the breakdown of the forms.
The color used for analytical cubism tended to be
tan, brown, grey, cream, green, or blue.
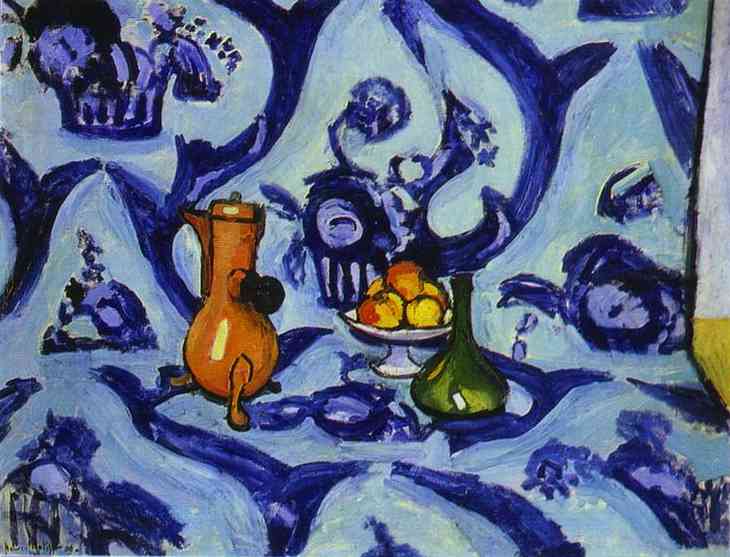
Fauvism (1905-1908):
Only lasted for a 4 year time period starting in 1905.
Fauvism means "wild beast", but it still is simple.
It got it's name because of the bright and unusual colors it used.
Synthetic Cubism style had smooth and rough edges contrasted together.
Color was important to make objects larger and more decorative.
Some paintings were collages with newspaper and paint for texture.
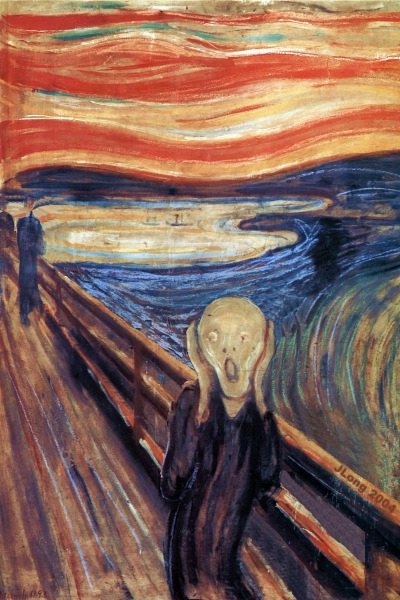
Expressionism (1905-1925):
Expressionism was a style the emphasized artist's emotion. The style tended to be distorted. Violent colors and exaggerated lines showed the emotional expression that the artists were painting. Artists (click on the link for more info): Edvard Munch Futurism (1910-1919):
Futurism originated in Italy and became part of the modernist movement.
This style was inspired by cubism and is brilliantly colored with flowing brush strokes.
Futurism focused on speed, technology, and violence.
Artists (click on the link for more info):
Dadaism (1916-1924):
Dadaism originated in Switzerland and was a post- World War 1 movement in visual art
It was meant to be a protest against the barbarism of the war.
The art is random and has no meaning.
The meaning depends on the viewers perspective
Artists (click on the link for more info):
|
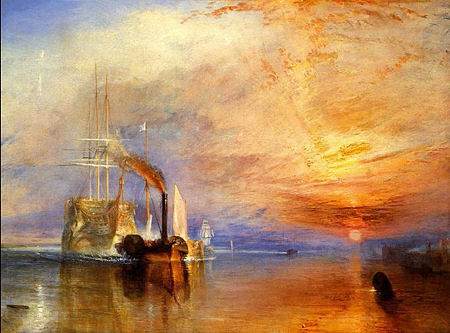 



 |